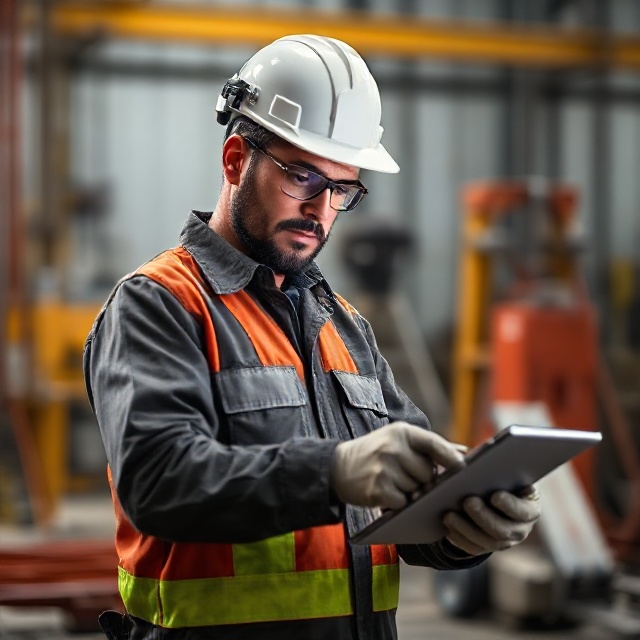
Surveying, also known as geomatics engineering, is a scientific and mathematical discipline that studies the shapes, sizes, and areas of locations and objects in space. It’s a fundamental field used in various areas, including:
- Civil Engineering and Architecture
- Astronomy and Geography
- Transportation and Environmental Planning
Surveying is a specialized branch of engineering focused on measuring the Earth’s surface, including its physical features, elevations, and structure. Professional architectural firms rely on surveying teams to plan and execute a wide range of engineering and construction projects.
History of Surveying
Surveying is not a new science; its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations.
- Ancient Times: The ancient Egyptians and Romans used rudimentary tools like ropes, chains, and rods to measure land areas, distances, and angles.
- 17th Century: The field evolved with the invention of more advanced devices like the theodolite, which allowed for more accurate angle measurements.
- 19th Century: Technological advancements like the plane table and the introduction of the transit greatly improved surveying techniques.
- 20th Century: The rise of electronic distance meters, Global Positioning Systems (GPS), and computer technology revolutionized surveying, making it significantly faster and more accurate.
Fields of Surveying
The field of surveying includes several professional specializations:
- Plane Geometry: Deals with two-dimensional shapes and structures.
- Spatial Geometry: Focuses on three-dimensional shapes and objects.
- Analytical Geometry: Utilizes mathematical equations and is essential for survey calculations.
- Geospatial Engineering: Involves studying and analyzing changes in specific locations.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Uses specialized technology to manage, store, and analyze geographic information.
- Geodesy: Measures dimensions like distances and elevations on maps and mathematical models.
- Geomatics: An integrated field that combines surveying with information technology to analyze geographic data.
The Role and Tasks of a Surveyor
A surveyor performs precise and professional tasks across various fields. Their key responsibilities include:
- Mapping and Boundaries: Surveyors determine geographical locations, define property boundaries, and create maps for land, roads, and public facilities.
- Measurement: They use specialized tools to measure angles and distances of specific areas, including buildings and landmarks.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Surveyors use tools like measuring tapes, rulers, remote sensors, and GPS to collect data on terrain, elevations, and structures. They then analyze this data using computer software to create detailed maps and 3D models.
- Land Suitability: They assess land for its suitability for specific uses like construction, mining, or agriculture by analyzing its physical and chemical properties such as durability, density, and strength.
- Project Planning and Design: Surveyors provide crucial data used by engineers to prepare maps and plans for various projects, including buildings, bridges, and tunnels.
Tools Used in Surveying
Modern surveying relies on a mix of advanced and traditional tools:
- Electronic Instruments: This includes highly accurate GPS devices, radar, sonar, and digital cameras used for precise distance and angle measurements.
- Optical Tools: Tools like telescopes, photographic cameras, and binoculars are used to capture visual data.
- Manual Tools: Traditional tools such as tapes, stakes, and spirit levels are still used, although they are less common due to their time-consuming nature.
- Mechanical Tools: Tools like hammers and stakes are used to support other instruments and define angles and elevations.
It is crucial for a professional surveyor to not only have the right tools but also the expertise to apply these advanced technologies effectively and accurately.
Types of Surveying
The field of surveying includes several distinct types, each with a specific purpose:
- Topographic Surveying: This type measures and maps natural and man-made features on the landscape, such as mountains, valleys, and roads. It’s used for creating maps and for civil and architectural design.
- Hydrographic Surveying: This involves mapping and measuring bodies of water like oceans, rivers, and harbors. It assesses water depth, quality, and the ocean floor.
- Construction Surveying: This is essential for building roads and other structures. It uses specialized equipment to ensure that construction projects are built according to plan.
- Geodetic Surveying: This is a highly accurate method for measuring large areas, distances, and elevations. It’s used for mapping large land boundaries and determining geographical coordinates.
- Engineering Surveying: This type involves analyzing data about the physical environment for planning and creating civil engineering projects.
Applications of Surveying
Surveying is a critical component of many industries and projects:
- Construction: Surveying is fundamental for building projects, including roads, buildings, and bridges, as it ensures that structures are built accurately according to the plan.
- Archaeology: Surveyors help document archaeological sites and artifacts, and identify areas of potential archaeological importance.
- Cartography (Map Making): Surveying is essential for creating accurate maps and charts by providing precise measurements and data about the Earth’s surface.
- Mining: Surveying is used in mining to identify deposits of raw materials and to monitor the progress of excavation and exploration.
In conclusion, surveying is a vital field with diverse applications that are essential for the planning, design, and execution of engineering projects. The professional skills and advanced tools used by surveyors ensure accuracy and efficiency across various industries.
connect now
INFO@ALEBTEKAR.COM.SA
0540007320
920004058